what is it?
It is a disease that is caused by the inability of the esophagus to contract and push food into the stomach (absence of peristaltic contractions) and by the lack of relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter (muscular thickening located at the junction of the esophagus and stomach that It functions as a valve and allows the passage of food to the stomach and prevents the contents of the stomach from ascending into the esophagus), which prevents the correct passage of food to the stomach.
Its exact cause is unknown.
There is no effective medical treatment and it is reserved only for very elderly patients or patients with very high surgical risks.All current treatments are aimed at weakening the lower sphincter of the esophagus to relieve dysphagia.The endoscopic intrasphincteric injection of botulinum toxin that has been used previously should not be used today, since it achieves results in only 50% of cases, and its effects are transitory (less than 6 months).The two commonly accepted treatments are endoscopic and surgical.Its objective is to reduce the pressure of the lower esophageal sphincter so that food passes into the stomach more easily, with excellent or good results in 90% of cases.Endoscopic dilation is carried out by inflating a balloon at the junction between the esophagus and the stomach, usually with the patient sedated and under radiological control.The initial rate of improvement is high, up to 80%, but symptoms return in 40% of patients within two years.
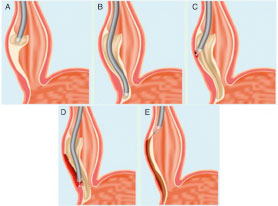
The most effective today is the surgical treatment based on the circular cutting of the circular muscular layer of the esophagus (myotomy) in a variable length (5-10 cm).It can be done laparoscopically, or endoscopically (through the mouth), which achieves even better results with less pain and fewer complications.This is the Technique called peroral myotomy or (POEM).The POEM that we perform replaces the Heller myotomy, which must always associate a Nissen or Toupet-type antireflux technique with a shorter stay, better recovery and fewer risks.The POEM consists of making a small incision in the esophageal mucosa, about 2 centimeters, to subsequently create a tunnel in the submucosa between the mucosal and muscular layers of the esophagus.
Later the tunnel extends until it reaches the stomach.
At this time, the myotomy, or cut of the muscular layer, is performed, leaving the mucosa intact, which will later cover this cut.The technique ends by suturing the entry hole to the mucosa with staples.The entire procedure is performed through the mouth, so at the end, there are no wounds or scars and recovery is better.It is performed in the operating room and under orotracheal intubation and lasts approximately 90 minutes, with expected discharge in less than 48 hours.
You have two very obvious advantages over classic laparoscopic surgery: POEM can be performed even when the patient has undergone surgery through a previous myotomy (whether endoscopic or laparoscopic), which is very complex or impossible by surgery.
And the length of the myotomy can also be regulated, which is particularly important in cases of achalasia type III and in other motor disorders of the esophagus, such as diffuse esophageal spasm or nutcracker esophagus, which have very poor results with classic surgical techniques..
In the Unit, both dilation and POEM are performed, which is usually the best treatment to offer to patients and which is currently available in very few National centers and none in the private sector.


